Carrageenan is used in multiple branches of food industry, for instance dairy products (butter, cream, ice-cream, yoghurt), meat products (pâté, cold cuts, sausages), bakery products, fruit products (jam, jelly, marmalade) and pet food. The reason for this is because of the gelling, thickening and stabilizing properties. Carrageenan could be also used as a vegetarian and vegan substitute for gelatin in some products.
Previously, there were some doubts whether is it safe to use for humans. To answer the question if and to what extent carrageenan effects the organism, multiple studies have been conducted. The results show that carrageenan is safe to use. Furthermore there is no daily limit for its consumption.
There are three main types of carrageenan: Kappa, Iota and Lambda. Kappa carrageenan creates strong, rigid gel, Iota creates soft gel, whereas Lambda does not gel, but can be used as a thickener for dairy products.
In recent times, most of the new releases containing carrageenan are desserts and ice cream, followed by RTD coffees. Details could be seen on the graph below.
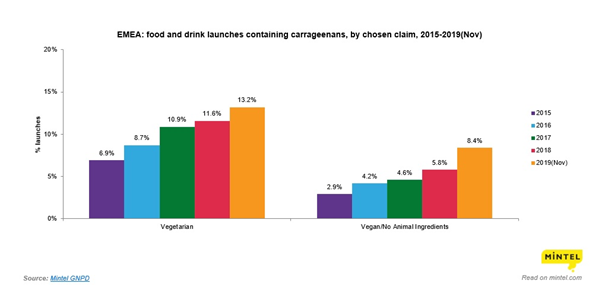
In addition, more and more vegetarian and vegan products containing carrageenan are released, as it could be seen on the graph below:
It is worth mentioning that food manufacturers do not add the excess of carrageenan to their products. According to the arrangements and recommendations made by the European Union, carrageenan can be added to food on a quantum satis basis. Quantum satis means it can be added without any restrictions, but in the minimum dose needed to achieve the intended technological result. Substances in this category are safe enough there is no need for a maximal limit when added to food products.




